"Entrepreneurial aspirations" to hear the background of deciding to start a business, the conflict until the business gets on track, and the desire to realize through the business.
In the 14th meeting, we interviewed Mr. Ryu Ogawa, CEO of MOLCURE Inc., which provides AI molecular design services for pharmaceutical products.
【profile】
Ryu Ogawa , CEO of MOLCURE Inc.
Keio University Graduate School of Media and Governance Ph.D. (2016), MOLCURE Inc. CEO (2013)
In charge of "Basic Molecular Biology 1" and "Genome Analysis Programming" as a part-time lecturer at the Faculty of Environment and Information Studies, Keio University. Served as the leader of the Epigenetics Research Team at the Institute for Advanced Biosciences, Keio University, and developed a technology for predicting the formation position of DNA-protein structures using artificial intelligence. Received many awards such as the highest award in the business creation contest (2014) and The Venture representative from Japan (2016). Founded MOLCURE Inc. (drug discovery support venture) in 2013, and the company has adopted many NEDO "Next Generation Artificial Intelligence / Robot Core Technology Development" (2016).
[What's MOLCURE Inc.]
MOLCURE is a startup that creates new drugs by providing pharmaceutical companies with "peptide / antibody molecule design technology that integrates artificial intelligence, evolutionary molecular engineering, and experimental automation" and building a joint drug discovery pipeline. By using search technology, it is possible to discover excellent drug molecules with performance that is difficult to search with conventional methods. In addition, since MOLCURE's technology has achieved efficiency in obtaining more drug candidates in a shorter time, pharmaceutical companies can expect to "discover and increase the number of new drug candidate molecules," "shorten the drug discovery process," and "reduce R&D costs" by adopting our technology.
Childhood attracted to scientists by movie heroes
-First of all, could you tell us what made you decide to go on the path of biotechnology at university?
To talk about that, I go back to my childhood, but when I was in elementary school, there are occupations that everyone wants to be, such as "I want to be a firefighter" or "I want to be a soccer player". But I didn't have a profession that I really wanted to be. On the other hand, I want to be the liquid metal android "T-1000" that appears in the movie "Terminator 2", and I want to be the parasite "Miggy" that appears in the manga "Parasitic Beast". .. I had a longing for them who could freely transform themselves and think.
In my profession, I think the most compelling thing to do is a scientist. Most of the movies I watched at the time were heroes or scientists, and heroes were overwhelmingly popular with the children around me. In that, I vaguely thought, "Without scientists, heroes wouldn't be able to play an active role, and humankind would have been destroyed." "Scientists are cool."
-It's unique to think "I want to be" instead of "I want to develop".
And when I was in high school, I met "Ghost in the Shell". Technology that transmits information from the human brain to a computer in real time and communicates between the brains is emerging, and it is a small molecular-level machine called a "nanomachine" that makes this possible. It is a setting that enables communication by filling the brain with nanomachines. I became absorbed in that view of the world and began to think, "I want to make nanomachines!"
In fact, this science fiction-like world view has already been realized in the natural world. When I was in high school, I had the opportunity to investigate viruses, but I learned about the function of viruses, which is to "overwrite and rewrite human blueprints and make them mistakenly make a lot of viruses in their bodies." I was surprised. I think we're already doing something close to nanomachines. Compared to human beings, which have only about 5 million years of history, life has been field-tested on the earth for 4 billion years, and the structural design of molecules has evolved to the point where life itself can do it.
If you want to make nanomachines, you need to learn from biomolecules. With that in mind, I proceeded to the field of advanced life science and continued my research with my master's and doctoral degrees.

-When did you start researching "Molecular design with AI", which is the core technology of MOLCURE?
Initially, we were developing AI software for scientists to use. Keio University's Institute for Advanced Biosciences, to which I belonged, was originally a computer science laboratory, but it led the research area of analyzing life information using computers. When I first joined the Institute for Advanced Biosciences, I was conducting research on intramolecular interactions that would lead to the basis of nanomachine development, but even using the world's largest database published at that time, molecular design I found it difficult. So I shifted to the field of omics analysis and made software for scientists that applied machine learning algorithms.
However, I was very disappointed that my father died of cancer while I was in school and I could not directly use it to treat my father. I want to contribute more directly to patients and society through my research. With that in mind, I decided to "make a drug for cancer" and returned to the area of molecular design.
-How is drug discovery by molecular design different from conventional drug discovery?
In the first place, there are "small molecule drugs" that use chemical technology and "biopharmacy (medium molecule / polymer drugs)" that use biotechnology, and the market size of biopharmacy has expanded in recent years. .. Among biopharmacy, there are "antibody drugs" that utilize the mechanism of antibodies produced by the immune function of the living body and "peptide drugs" that are shortly polymerized amino acids, and as therapeutic drugs for diseases for which there is no effective treatment method yet. It is expected.
For example, mouse immunity is used as the standard method for making antibody drugs for cancer. When human cancer cells or some of them are injected into a mouse, the body of the mouse activates immunity to counter foreign substances and produces antibodies. The standard method is to repeat the experiment many times to find an antibody that is effective for humans. However, it is said that the antibodies obtained by that method have been exhausted, and there are many drug discovery targets and drug discovery concepts where it is difficult to search for antibodies by the immune method in the first place.
If so, the drug discovery method based on molecular design is to design the molecule of the drug. Therefore, I focused on molecular design using AI. Biopharmacy has a much larger molecular weight and is more complex than low-molecular-weight drugs, making it difficult to design using conventional methods. Therefore, I decided to use AI to challenge the method of designing excellent molecules that are difficult to search in experiments. At that time, the words and technologies of AI and machine learning were not well known in the drug discovery field, and they had a strong experimental-driven way of thinking, so when we talked about the method of "designing molecules by machine learning," we could get angry. It was common.
Biopharmacy molecular design technology with AI that is unique in the world
-Why did you choose the path of "entrepreneurship" from there?
Among the several options, entrepreneurship was the way to realize my vision in the shortest possible time. There is no guarantee that university researchers will receive grants for research, and young researchers tend to have smaller funding. Since grants are taxes, they are invested preferentially in the priority areas that the country considers rather than in the areas that you want to do. On the other hand, if you work for a pharmaceutical company, you have the task of constantly creating new drugs in line with the company's policy, and it is difficult to take on new challenges that were not in the company's policy at the time, such as molecular design using AI. , I thought that in-house politics would be necessary to get a budget.
I liked programming, so I've been involved in IT startups for seniors and acquaintances since I was an undergraduate student. As a core member, I was in charge of raising funds from VCs, and based on that experience, I chose to start a business as the best way to realize my vision on my own initiative.
-It seems that it was founded by three people.
Yes. Since I specialized in biotechnology and AI, I formed a tag team with three members, one who is strong in robots and the other who is strong in design and business. Two people were in school, including myself, who was in the doctoral course. I thought that it is essential to automate experiments with robots in order to collect a huge amount of learning data for molecular design with AI. This is because if humans do it, efficiency and reproducibility will inevitably be inferior. Therefore, the combination of bio x robot x AI was a must for business.

-Did you have any difficulties in starting the business or did you have any obstacles?
I'm the type that I don't think is "hard", but I have had some trial and error in advancing the business. For example, at that time, the introduction of IT to pharmaceutical companies, which I was thinking of as a service introduction destination, was not as advanced as I had imagined, and I was at the stage of "what is machine learning?" Therefore, at the beginning, I focused on working with universities and research institutes.
AI has begun to attract attention at pharmaceutical companies, and there was a problem when it came time to introduce it. At first, I was thinking of providing AI itself to pharmaceutical companies, but it was difficult for pharmaceutical companies to move AI by themselves. Also, the cost and time required to order an experiment for collecting learning data from a university or another company was greater than I had imagined. Therefore, we turned to a method of providing molecular design drawings to pharmaceutical companies by running from experiments to AI operations in-house. Currently, it has been introduced by major pharmaceutical companies in Japan and overseas, and has a total of 10 projects from 7 companies.
-Is there competition in the area of drug molecule design with AI?
For small molecular weight drugs with small molecular weight, some companies are working on molecular design with AI. However, in the field of biopharmacy such as antibodies and peptides, even if we observe the world widely, we are able to provide practical level services that can design molecules with performance higher than the molecules searched by experimental experts. I think that is the only company in the world.
In the cases so far, AI can be used to design molecules with 100 times more binding force than the molecules obtained from experiments. Compared to conventional biopharmacy development, it will be possible to search and design 10 times more excellent candidate molecules in about half the time. Some pharmaceutical companies think that introducing our service will replace their experimental team, but that's a misunderstanding. MOLCURE 's AI is customized and provided for each project and pharmaceutical company, and in many cases, an AI that is additionally learned by the craftsmanship of the experimental team of the pharmaceutical company is built exclusively. Therefore, the experimental teams of each pharmaceutical company and AI have a cooperative relationship, and each pharmaceutical company will have a different personality. It is possible to let AI learn the skills of craftsmen and amplify the results of experimental teams and projects with AI.
Series C round for organizational expansion
-Please tell us about the history of financing so far.
We completed Series A in 2014, Series B in 2018, and Series C in June this year. For Series C, JAFCO made the first decision, and as a lead investor, he led the financing of a total of less than 800 million yen.
-What is the purpose of this funding?
We are strengthening the "business / sales side" to expand alliances with pharmaceutical companies around the world and the "capacity side" to receive projects. The number of employees was about 20 at that time, but since there was no business team in the company, the main purpose was to expand the organization to improve sales force and capacity. In addition to peptides and antibodies, we will continue to promote the expansion of modalities to nucleic acid drugs such as RNA aptamers and DNA aptamers, and cell therapy areas such as CAR-T cells.
-What was the deciding factor for receiving the investment from Jafco?
When deciding whether or not to invest in a company like us, how much contract you have with a pharmaceutical company is an important factor in making a decision. However, in this industry, it is often the case that the contract content cannot even disclose the fact that the contract is made. While many VCs asked to present a contract, JAFCO responded sincerely at the convenience of our company despite being the largest. I have been acquainted with him since the company was founded, and I have had several interviews with him, so I heard that he trusted me and decided to invest.
-What kind of support do you expect from Jafco?
Due diligence itself was a part of the support that MOLCURE learned, so it feels like we have already received support even before the investment. Mr. Miura, the capitalist in charge, is from biotechnology and has a deep understanding of the business, and is very polite and serious. In the future, we would like to receive the support of the business side such as IPO, and list the company by the end of 2024.
-Is there anything important in hiring human resources to expand your organization?
We are a company that values scientific thinking and flat discussions, so I would like people who like science to join us. As for the business human resources that we want to strengthen most, we would like to hire people who can design products, contracts and sales from a creative perspective, how to combine our technology into products and spread it to the world. As for the technical field, there is no particular special field as long as it seems to be useful for molecular design. It is a flat organization where each team of bio, robot, and AI can have free and open discussions, and half of the employees are foreign nationals. I think you can have an experience that you can't get anywhere else.
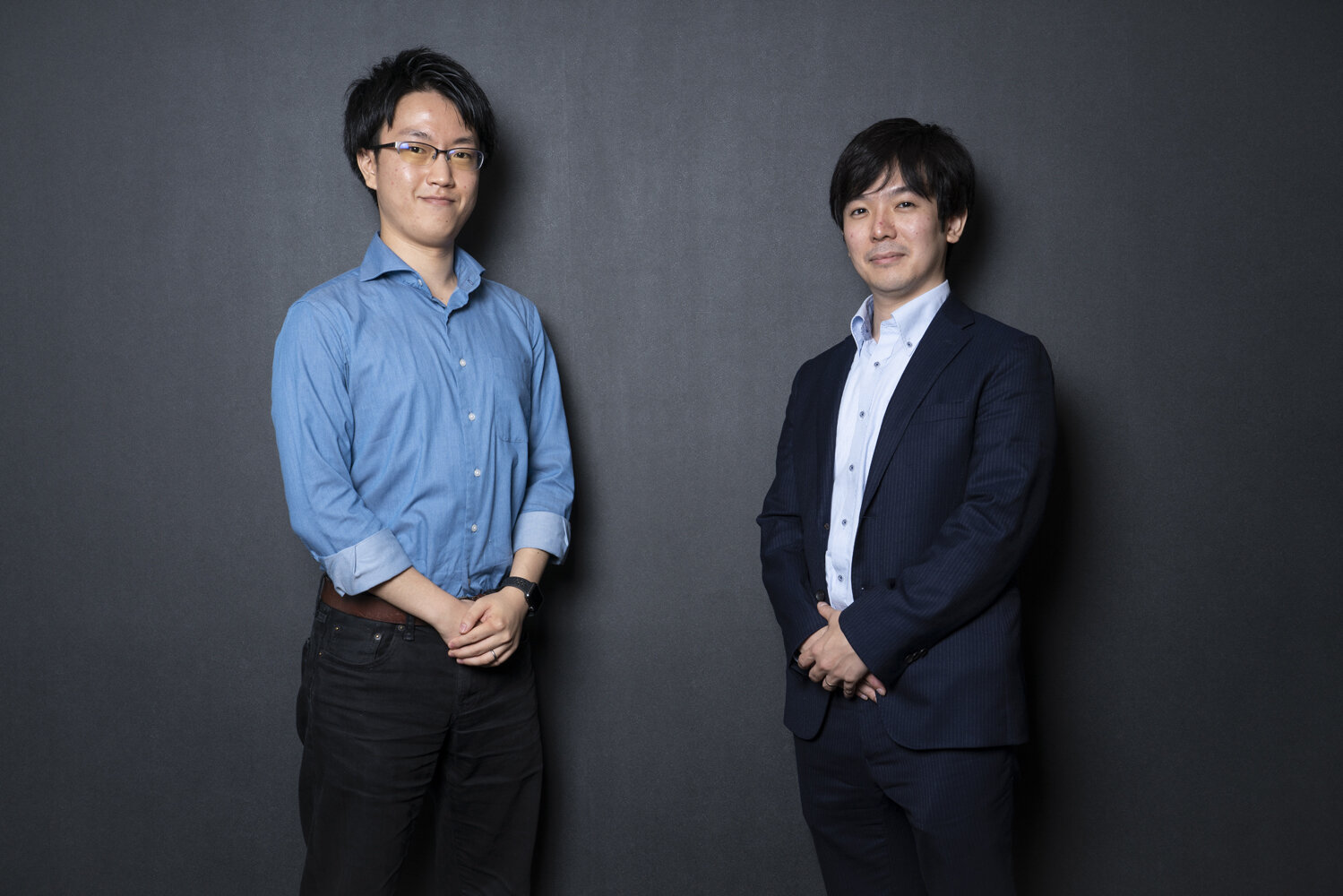

Mr. Ogawa and Kengo Miura, supervising JAFCO capitalist (left)
Science and business are not different
-Please tell us about your future vision for MOLCURE.
As a premise, we aim to be a company where all of our clients, employees, VCs, supporters, and everyone else can say, "I'm glad I was involved in MOLCURE." On top of that, we would like to realize a world where drug molecules can be designed as a matter of course, and a world where therapeutic drugs are available for all diseases.
-Mr. Ogawa, a scientist and manager, what is the secret to balancing the two perspectives?
I don't think science and business are completely different. I think that there are actually many common items used in both science and business, such as the idea of a bottleneck, the PDCA cycle method, and the writing of concepts. In science, you need to have the maximum knowledge of your area of expertise, but the same is true for business, and I think it is important to observe and know a lot of business-specific structures that you are targeting. increase. For example, when a contract is submitted to a pharmaceutical company, what kind of discussions are held at internal meetings, what kind of dynamics work from end users, and what kind of technology and contract contents are they happy with? I think it is important to hold them down properly.
-Finally, do you have a message for everyone who wants to start a business?
The most important thing is to take the best measures for what you want to do. If you forcibly start a business, distortion will occur somewhere, so I think it would be better to start a business if starting a business is the best option after thinking rationally. In addition, many unexpected phenomena occur as we proceed with our business. Not only does it not go according to the first scenario, but it also needs to be changed every moment even in a rethinking scenario. Always observe the surroundings and update the hypothesis. I think that people who can maintain that attitude, and those who do not suffer from it, are people who are compatible with entrepreneurship.